What is a Virtual Private Network or VPN?
A virtual private network is a computer networking tool to send and receive data over shared or public networks. VPNs act as though their devices are directly connected to the private network.
Who uses a VPN?
A user who needs to extend a private network across a public network could use a VPN. That VPN would offer the following benefits:
- Secure web traffic.
- Protect anonymity.
- Counter snooping.
- Hamper theft.
- Prevent misuse of data.
Where would you use a VPN?
A VPN can be used on any computer over which a person needs to send and receive information privately.
When would you use a VPN?
A VPN creates an encrypted “tunnel” between a device and a remote server operated by a VPN service. The data is routed through this tunnel; therefore, all data is secure from prying eyes. Also, the computer appears to have the IP address of the VPN thus masking the identity. Once it exits, the data is hard to trace because it appears to be coming from the VPN server.
Why would you use a VPN?
A virtual private network would be used when data needs to be protected and secured by anonymity.
How to set up VPN access?
Refer to the specific instructions for your VPN. The following are basic steps for setting up a VPN on a Windows 10 machine.
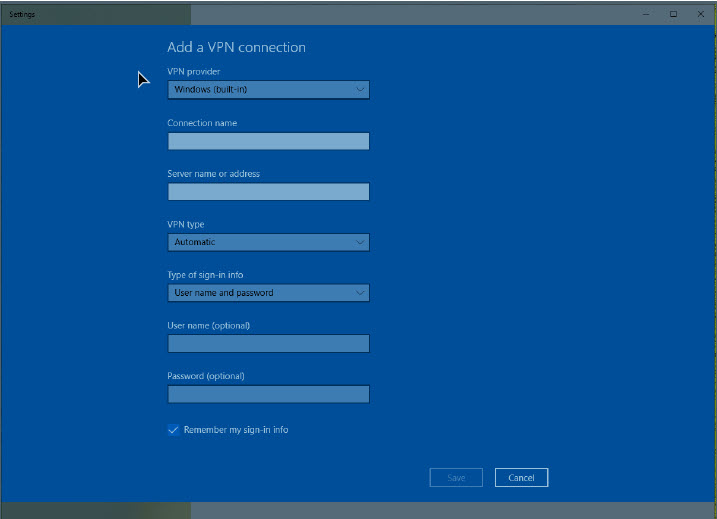
Complete the following steps to set up VPN access for Windows 10:
- Type “VPN” into the Windows search bar under the Start Menu.
- Select “VPN settings” to configure your VPN.
- Click “Add a VPN connection” if you don’t already have one.
- Enter the information specific to your VPN connection.
- Click “Save” to confirm your connection.